General Security Considerations
- Communications
- Authentication
- Authorization
- User Managed Provider Access - Using XACML
- Audit Logging
- Digital Signatures
- Security Labels
- Data Security Policies
CollabKare transactions often make use of patient-specific information which could be exploited by malicious actors resulting in exposure of patient data. For this reason, all CollabKare transactions must be secured appropriately with access to limited authorized individuals, data protected in transit, and appropriate audit measures taken.
The security system includes the following subsystems:
- Authentication: identifies and authenticates the user
- Access Control decision engine: decides whether CN operations are allowed
- Audit Log: records actions to allow for subsequent review and detection of intrusion or inappropriate usage
Communications
TLS/SSL SHOULD be used for all production data exchange. The TLS/SSL communications are established prior to any HTTP,HTTPS command/response, so the whole CN interaction is protected by the SSL/TLS communications. The security of the endpoints of the TLS/SSL communications must be risk-managed, so as to prevent inappropriate risks (e.g. audit logging of the GET parameters into an unprotected audit log).
Authentication
When user login with their Credentials (user id and password), If Authentication server verified successfully then UAA generates OAUTH2 Token(Access Token).
Roles :
- Patient
- Parent
- Guardian
- Provider
- System Support
- Staff
Authorization
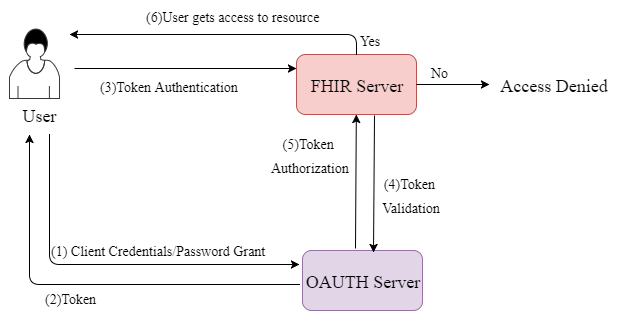
After completion of successful Authentication, FHIR server can verifies the OAUTH2 Token is valid or not. If it is Valid then User will get the full Access to resources.
User Managed Provider Access - Using XACML
XACML is a declarative access control policy language implemented in XML as well as a processing model that describes how to interpret the policies. Compared with an access control list (ACL), XACML provides flexible, generic and extensible access control.
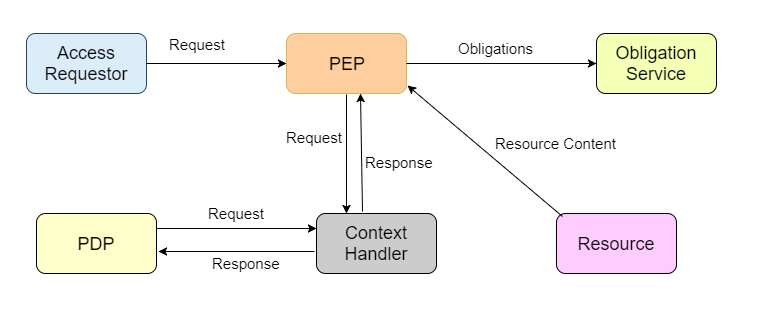
- A user(in XACML terms, a subject) requests data from a specific network resource(a file system, server, database or web service).
- PEP: The query goes to entity protecting the resource called a Policy Enforcement Point or PEP.
- Create XACML request: The PEP uses the XACML request language to create a request based on the attributes of the subject, action, resource and other relevant information.
- PDP: The PEP sends this request to a Policy Decision Point(PDP).
- Existing access control policies: The PDP retrieves applicable policies(written in XACML).
- Request Match Policy: The PDP compares the request against policies and determines whether access should be granted.
- The answer (match or no match) goes back to the PEP.
- PEP determines whether access is authorized.
- If Match, it permits access by the user.
- If No Match, it denies user access.
The rules behind the access control decision are often very complex, and potentially depend on information sourced from:
- Client, such as user identity, user role, location, level of assurance
- Resource, such as confidentiality, sensitivity, type of data, date ranges covered by the data, author of the data
- Patient, such as the patient identity, patient relationship to the user, patient consent policies
- Context of the transaction, system identity, time-of-day, purpose of use, workflow state, and transport security
Access Control Considerations
The CN RESTful API provides a number of ways that a client may request or create information. When designing a system to authorize access to information, all potential access methods must be considered. They include the following:
- The basic CRUD methods on resources. A security implementation must evaluate whether a client is allowed to read, update create or delete a given resource.
- A security implementation must consider whether a client has the permission to access the resource being searched
- Several resources, including Bundle, Composition, Group and List, are designed to contain other resources. A security implementation should consider whether access to an individual resource, such as a Bundle, should permit access to all resources contained within the resource.
Access Denied Response Handling
The Access Denied condition might be because of missing but required Authentication, the user is not authorized to access the endpoint, the user is not authorized to access specific data, or other policy reasons.
- Return a 200 ok for “Success”
- Return a 404 “Not Found”
- Return a 403 “Forbidden”
- Return a 401 “Unauthorized”
Audit Logging
CN provides an AuditEvent resource suitable for use by CN clients and servers to record when a security or privacy relevant event has occurred. This form of audit logging records as much detail as reasonable at the time the event happened. Audit Logging is used as Centralized logs, it will maintain all the system logs(like login, logout, etc.). It is implemented using ELK Stack. Where ELK collects all the logs. In ELK
- E - ElasticSearch used for Log Search and Analysis.
- L - Logstash used to collecting, parsing, and storing logs for future use.
- K - Kibana used to Visualize the logs.
With regard to HTTP logs, implementers need to consider the implications of distributing access to the logs. HTTP logs, including those that only contain the URL itself, should be regarded as being as sensitive as the resources themselves.
Digital Signatures
Digital Signature is needed to prove authenticity, integrity, and non-repudiation CN Resources are often parts of Medical Record, or are communicated as part of formal Medical Documentation. As such there is a need to cryptographically bind a signature so that the receiving or consuming actor can verify authenticity, integrity, and non-repudiation. This functionality is provided through the signature element in Provenance Resource. Where the signature can be any local policy agreed to signature including Digital Signature methods and Electronic Signature. We are using some signature types as:
- Client
- Web-GUI
- Organization
Security Labels
Security labels are only a device to connect specific resources, bundles, or operations to a wider security framework; a full set of policy and consent statements and their consequent obligations is needed to give the labels meaning. As a consequence of this, security labels are most effective in fully trusted environments - that is, where all trading partners have agreed to abide by them in a Mutual Trust Framework. Note also that security labels support policy, and specific tagging of individual resources is not always required to implement policy correctly.
| Sensitivity Category | Code | Display | System | OID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Social History | ||||
| ETH - substance abuse information sensitivity | 160573003 | Alcohol intake (observable entity) | http://snomed.info/sct | 2.16.840.1.113883.6.96 |
| TBOO - taboo | 229819007 | Tobacco use and exposure (observable entity) | http://snomed.info/sct | 2.16.840.1.113883.6.96 |
| SEX - sexuality and reproductive health information sensitivity | 118200004 | Finding related to sexual state (finding) | http://snomed.info/sct | 2.16.840.1.113883.6.96 |
| DRGIS - drug information sensitivity | 228366006 | Finding related to drug misuse behaviour (finding) | http://snomed.info/sct | 2.16.840.1.113883.6.96 |
| PSY - psychiatry information sensitivity | - | psychiatric History | - | - |
| LIVARG - living arrangement information sensitivity | 20733006 | Living place (observable entity) | http://snomed.info/sct | 2.16.840.1.113883.6.96 |
| MARST - marital status information sensitivity | 125680007 | Marital status (observable entity) | http://snomed.info/sct | 2.16.840.1.113883.6.96 |
| SDV - sexual assault, abuse, or domestic violence information sensitivity | 429746005 | History of domestic abuse (situation) | http://snomed.info/sct | 2.16.840.1.113883.6.96 |
| GENDER - gender and sexual orientation information sensitivity | 66621004 | Sexual orientation (observable entity) | http://snomed.info/sct | 2.16.840.1.113883.6.96 |
| Patient | ||||
| DEMO - all demographic information sensitivity | 365449009 | Demographic history finding (finding) | http://snomed.info/sct | 2.16.840.1.113883.6.96 |
| DOB - date of birth information sensitivity | 184099003 | Date of birth (observable entity) | http://snomed.info/sct | 2.16.840.1.113883.6.96 |
| MARST - marital status information sensitivity | 125680007 | Marital status (observable entity) | http://snomed.info/sct | 2.16.840.1.113883.6.96 |
| PRS - patient requested sensitivity | 183995001 | Patient requested procedure (situation) | http://snomed.info/sct | 2.16.840.1.113883.6.96 |
| RACE - race information sensitivity | 103579009 | Race (observable entity) | http://snomed.info/sct | 2.16.840.1.113883.6.96 |
| REL - religion information sensitivity | 160538000 | Religious affiliation (observable entity) | http://snomed.info/sct | 2.16.840.1.113883.6.96 |
| Diagnostic Report | ||||
| DIA - diagnosis information sensitivity | 439401001 | Diagnosis (observable entity) | http://snomed.info/sct | 2.16.840.1.113883.6.96 |
PurposeOfUse
Reason for performing one or more operations on information, which may be permitted by source system’s security policy in accordance with one or more privacy policies and consent directives. Usage Notes: The rationale or purpose for an act relating to the management of personal health information, such as collecting personal health information for research or public health purposes. We are using the below codes:
| Code | Display | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| TREAT | treatment | To perform one or more operations on information for provision of health care. |
| HPAYMT | healthcare payment | To perform one or more operations on information for conducting financial or contractual activities related to payment for provision of health care. |
| HRESCH | healthcare research | To perform one or more operations on information for conducting scientific investigations to obtain health care knowledge. Use of the data iincludes basic and applied research such as biomedical, population origin or ancestry, translational research, and disease, discipline, specialty specific healthcare research and clinical trial research. |
Data Security Policies
We are using security protocols such as HIPAA and GDPR.
- GDPR means General Data Protection Regulation, it is a protocol which is used for more Privacy and Security. The Privacy Principles that are generally included in many standards and guidance are inclusive of giving the Individual the right of Access, the right of Correction, and the right to control how their data are used.
- The HIPAA audit protocols – which analyze the processes, controls and policies relating to privacy, security and breach notification.